Ah, the age-old question: Tea or Coffee? For many people, it is a daily dance between the energizing kick of coffee and the soothing embrace of tea. Aside from personal preference, the differences in caffeine content and interactions with our bodies reveal an intriguing science.
Buzz Levels and Effects: An Overview

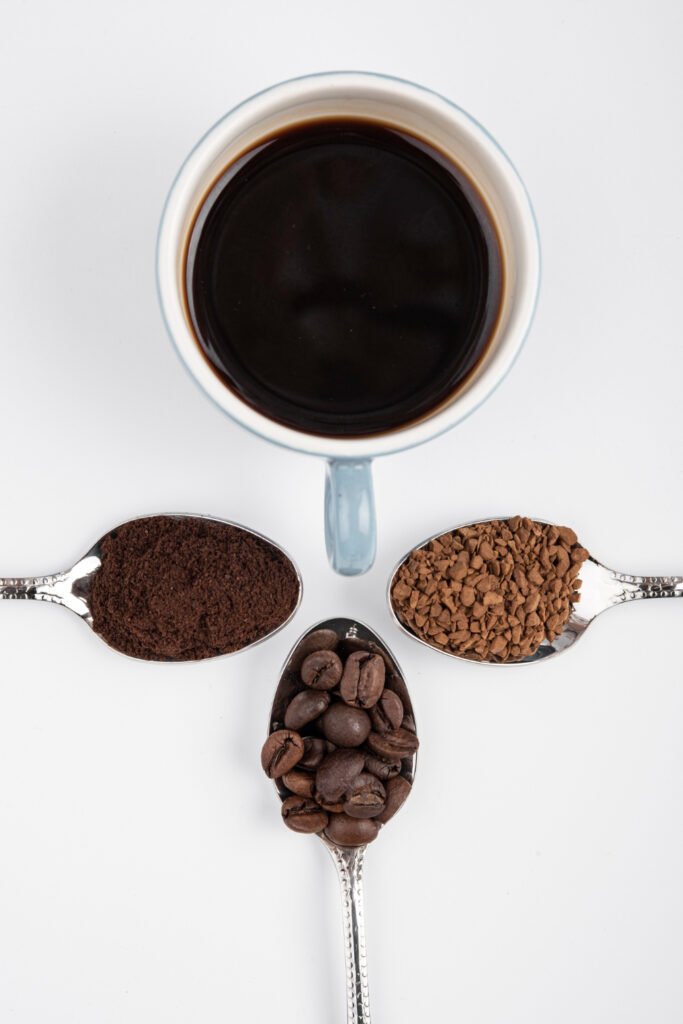
Coffee's Jolt: A Rapid Ride on the Caffeine Rollercoaster.
Coffee’s caffeine hit is like a rocket launch. Its high caffeine content, combined with the presence of chlorogenic acid, promotes faster absorption. Within 30 minutes, caffeine enters your bloodstream and binds to adenosine receptors in your brain. Adenosine typically causes drowsiness, but caffeine inhibits its effects, causing the release of adrenaline and dopamine. This cocktail of hormones leads to:
- Increased alertness and focus: You feel sharp, energized, and ready to face challenges.
- Enhanced physical performance: Muscles get a boost, making workouts feel easier and more efficient.
- Improved mood: Dopamine’s surge can elevate mood and motivation.
- Jitters and anxiety: Excess adrenaline can cause nervousness, restlessness, and shakiness.
- Insomnia: Drinking coffee too late in the day can disrupt sleeping patterns..
- Crash and burn: As caffeine wears off, it can lead to fatigue, headaches, and even withdrawal symptoms.
- Additionally, coffee can also increase heart rate and blood pressure, so it’s important to drink it in moderation

Tea's Gentle Rise: A Sustained Symphony of Focus and Calm
- Sustained focus and clarity: You have a constant alertness without the jitters, which is ideal for prolonged attention tasks.
- Improved mood and reduced stress: L-theanine’s calming effect counteracts the caffeine buzz, promoting relaxation and lowering anxiety.
- Enhanced creativity: Alpha brain waves have been linked to increased creativity and problem solving abilities.
- Subtle effects: You may not feel the immediate jolt of coffee, but the focus and calmness can be just as effective over time.
- Lower overall caffeine kick: If you want a strong pick-me-up, coffee may be a better option.
- Individual sensitivity: Because some people are more sensitive to caffeine than others, the effect of tea varies according to your body chemistry.

Research reveals the benefits (and drawbacks).
Science supports our anecdotal experiences. Studies have found that moderate coffee consumption improves cognitive function, memory, and athletic performance. Tea, which contains L-theanine, has shown promise in relieving stress and anxiety while improving focus. Both beverages contain antioxidants and have potential health benefits, such as lowering the risk of heart disease and cancer. However, excessive consumption of either can result in insomnia, tremors, and dependence.
But Why Caffeine? A Plant's Defense and Our Human Craving
Plants such as coffee and tea do not give us a cup of alertness out of kindness. Caffeine works as a natural pesticide, deterring insects and herbivores. For us humans, however, that insect repellent became a favorite stimulant. According to studies, our ancestors discovered the benefits of caffeine through trial and error, noticing increased energy and focus after consuming caffeinated plants. Over time, humans developed a taste for caffeine and began to cultivate plants with higher caffeine levels. This eventually led to the development of coffee, tea, and other caffeinated beverages.
Choosing Your Cup: Tailoring Caffeine for Your Needs
So, which team are you on? The choice doesn’t have to be binary. Understanding the differing caffeine profiles allows you to tailor your buzz to the occasion. Do you need a boost before your morning workout? Coffee’s quick jolt might be your thing. Need to maintain focus throughout a long workday? Tea’s gentle rise and consistent clarity may be ideal. Are you feeling stressed? Tea’s calming L-theanine can offer a soothing reprieve. Finally, the ideal cup is a personal balance of taste, desired effect, and individual sensitivity.
So, the next time you reach for a mug, remember that it is more than just a hot beverage; it is a science experiment waiting to be enjoyed. Enjoy the one-of-a-kind caffeine tango provided by these ancient plants, whether you are Team Tea or Team Coffee.
Unleashing the Caffeine Beast: Brewing Techniques and Their Power.
Aside from the inherent differences in caffeine content, how you brew your ideal cup can have a significant impact on how much of that sweet (or sometimes bitter) nectar enters your body. Let’s explore some brewing techniques and their caffeine power play:
Coffee
- Temperature: Hotter water = more caffeine extraction. So, that French press bubbling at 195°F (90°C) will likely pack a bigger punch than a chilled cold brew.
- Grinding: Finer grinds increase surface area, allowing for greater caffeine extraction. Thus, an espresso grind will extract more than a coarse French press grind.
- Steeping Time: The longer the coffee grounds are in contact with the water, the more caffeine is extracted. So, that quick drip coffee might have less caffeine than a slow pour-over.
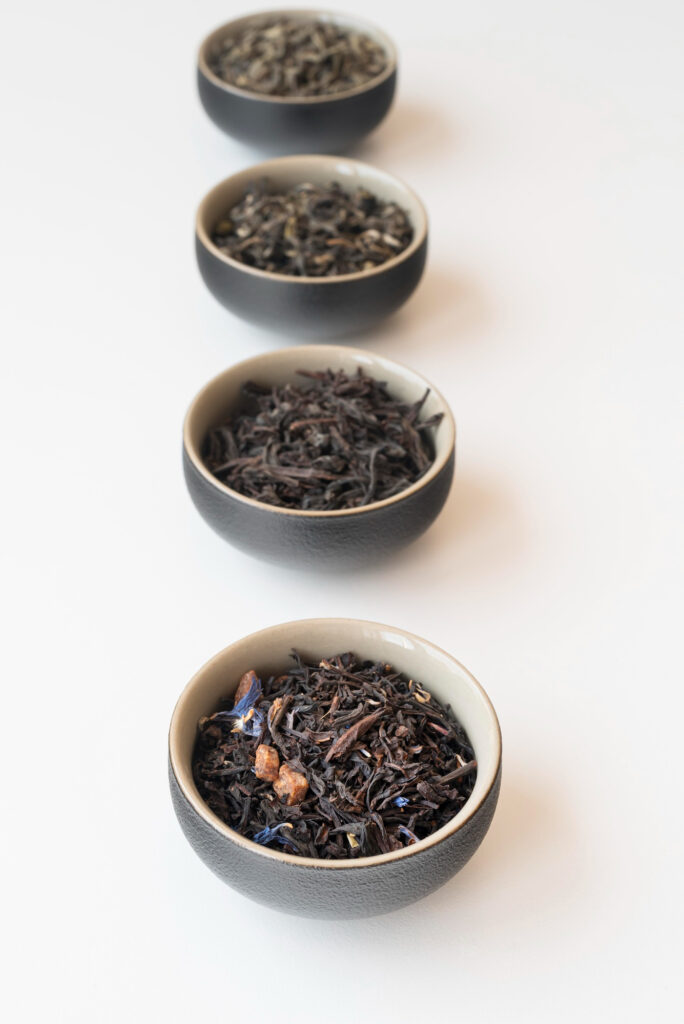


- Water Temperature: Similar to coffee, hotter water extracts more caffeine. However, different teas have different ideal temperatures. Black tea thrives at 195°F – 212°F (90°C – 100°C), while green tea prefers a gentler 176°F (80°C).
- Steeping Time: Just like coffee, longer steeping equals more caffeine. But over-steeping can lead to bitterness, so stick to those recommended times! Black tea shines at 3-5 minutes, while green tea is happy at 2-3 minutes.
- Leaf Size: Whole leaves release caffeine slower than broken leaves. So, those fancy whole leaf oolongs might have less caffeine than your everyday black tea bags.

